Over a year ago, workforces across the globe were required to work from home to ensure their safety during the pandemic. This meant that IT administrators spent a majority of 2020 trying to figure out the best way to connect a distributed workforce while maintaining the overall security of their organization’s network.
The organizations that have adapted well to keeping their remote workforces secure have even been able to reduce their office space expenses in major cities. On the flip side, many organizations have been challenged with implementing necessary security measures, especially because of the surge in the use of personal devices, including smartphones, laptops, and tablets.
“Mobile endpoint security is the process of securing the mobile devices used in organizations by configuring security protocols and policies to ensure safety, and achieve compliance with security standards.”
With the second and third waves of the pandemic hitting several countries, it is safe to say that remote work is here to stay. Therefore, it is crucial for every organization to start implementing effective mobile endpoint security.
What is Mobile Endpoint Security?
Mobile endpoint security is the process of securing the mobile devices used in organizations by configuring security protocols and policies to ensure safety, and achieve compliance with security standards. Generally, it involves the IT Team using a Mobile Device Management (MDM) tool to manage the personal and corporate mobile devices used in the organization, ensuring security of data at rest, in transit, and in use.
Mobile Endpoint Security: A Vital Component of Remote Work
Addressing mobile endpoint security is now a top priority for organizations everywhere since the sudden shift to remote work has accelerated the adoption of mobile devices in the workplace quite dramatically. Personal devices, including smartphones, tablets, and laptops have been brought to the forefront, and are key to maintaining employee productivity. Thanks to mobile devices, teams can stay connected, transfer critical knowledge, have video conferences, and enjoy flexible work hours, even if they are located miles apart.
“Mobile devices are favored by remote workers; however, these devices can be the most vulnerable endpoints in corporate organizations.”
Because most employees already own a mobile device, the smooth adaptation of these devices enabled companies to avoid major downtime when lockdowns were initially announced. Even employees who work out of the office and at home still use their mobile devices for work. Moreover, the introduction of 5G technology is expected to increase the use of mobile devices by workforces since it provides them with high-speed internet even when working remotely.
The Risks Mobile Endpoints Pose to Your Organization's Security
Mobile devices are favored by remote workers; however, these devices can be the most vulnerable endpoints in corporate organizations.
- Devices without passwords: Passwords are the first line of defense on any device. However, for the sake of convenience, users tend to use their mobile devices without a password. When employees’ devices contain sensitive information, the lack of a password ensures data theft is easier. Moreover, several security standards mandate that sensitive data, like Personally Identifiable Information (PII), be password-protected at all times. If employees do not have a password on the device they use for work, it could result in a hefty compliance fine for the organization.
- Threats from foreign networks: While working remotely, employees may need to connect to unknown, public, or shared Wi-Fi. These connections are prone to cyber-attacks, such as man-in-the-middle attacks where the bad actor views and even manipulates the data sent to and from the connected device. A cybercriminal could potentially obtain an employee’s credentials this way, use them to log in to the organization’s network, and steal sensitive data.
- Mixture of corporate and personal data: Be it a personally owned bring-your-own device, or a corporate-owned device, a majority of employees end up using the same device for personal and corporate use. This can lead to personal and corporate files being indistinguishable from each other, making it tricky to manage corporate files without it being too intrusive for the end user. Furthermore, this can also mean that personal apps installed on the device could access sensitive corporate data, leading to data leaks.
- Malicious domains: Accessing untrusted sites or clicking on unsafe hyperlinks, even inadvertently, can install malware or spyware on the device. This malicious software is capable of silently exporting confidential information. It is no surprise that malware is one of the primary causes of corporate data leaks.
- Automated third-party cloud backups: Almost every application on mobile devices nowadays has cloud backup features to facilitate seamless work. However, sometimes sensitive corporate data can end up being automatically backed up to third-party cloud servers. This not only leads to the data falling in the hands of an unauthorized party, but also means that the sensitive data is now only as secure as the cloud itself and is subject to any cyber-attacks the cloud faces. This is risky because many data leaks are caused by vulnerabilities in cloud storage facilities.
- Unauthorized mobile endpoints: Remote work has required most workplaces to make its internal networks accessible over the internet. Without strict, around-the-clock monitoring, it is challenging for IT admins to prevent unauthorized devices from connecting to the network. This makes it easier for bad actors to connect to the organization’s network and steal data.
- Shadow IT: It can be tedious for the IT team to keep track and provision employees from multiple teams with the required apps in a secure way. This can drive employees to download requisite apps from untrusted third-party sites, essentially leading to sensitive data being accessible to unauthorized third-party app providers.
- Skipping updates: Employees might not always have the latest app and Operating System (OS) updates on their devices since patches cause device downtime and can consume considerable network bandwidth to download and install. Remote employees may be hesitant to invest the time to keep their devices up to date. This can leave the device openly vulnerable to cyberthreats that the patches aimed to fix.
- Email vulnerabilities: Cyberthreats can easily bypass the built-in security of cloud-based email services. Moreover, social engineering attacks have also become very popular, with many targeting employees working from home. Cybercrooks spoof their identity, attempting to gather credentials and other sensitive information from employees primarily through emails. Remote employees are more likely to take the bait from a phishing or spoofing cybercriminal because they feel more socially isolated than on-site employees. This makes it easier for bad actors to successfully breach corporate data.
- Obsolete devices: Out-of-date devices can prove to be a big crack in the security armor of organizations because they lack new patches and are vulnerable to several security threats from cybercriminals.
- Lost or stolen endpoints: Mobile devices can end up lost or stolen quite easily since they are compact. It is tricky to track and secure a lost mobile device, and when such a device carries sensitive organizational data, the device falling into the wrong hands can result in a data leak and a costly penalty for the organization.
What You Can Do To Stay Prepared and Protected
It may seem daunting to maintain security with multiple mobile endpoints used within the organization. Typically, mobile devices do not come configured with security features to match corporate standards right out of the box. Cyberthreats have evolved to a much greater extent, demanding robust, solid security measures. It is essential that mobile endpoint security is bolstered to fulfill compliance standards and keep the network safe.
This can be accomplished with an effective Mobile Device Management (MDM) solution that offers a unified console to manage different types of mobile endpoints across multiple platforms. This allows IT admins to optimize their organization’s security by focusing on the three major aspects of security: confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Confidentiality
Maintaining confidentiality involves disclosing sensitive information on a need-to-know basis and protecting it from unauthorized access. For instance, keeping personal information about a client behind a firewall constitutes maintaining its confidentiality. Let us assume a remote worker accesses those files from their mobile device during their course of work. To ensure the file is still protected, you can:
- Mandate password policies: Develop clear password policies and enforce them on every mobile endpoint used for work. This ensures that each device has at least a basic amount of security, and IT admins can rest easy without fear of a compliance breach.
- Block malicious domains and apps: To protect sensitive data from security threats, prevent access to known malicious sites and the installation of malware apps on mobile endpoints. IT admins can even alert employees to uninstall unsafe apps, and completely block the installation of apps from untrusted sources.
- Use a dedicated app for work: With MDM, IT admins can distribute a dedicated app to view corporate files, prevent the involvement of third-party app providers, and guarantee the safety of sensitive data.
- Secure email communications: MDM solutions can help ensure that employees are using a trusted email client to access emails and view attachments, secure protocols to communicate emails, and even filter out emails that have questionable HTML encoding, which is a common strategy used by spoofing cybercriminals.
- Track lost or stolen devices: If a device is reported lost or stolen, IT admins can track the geographical location of the device from the management console, and try to recover it to prevent sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands. If the device turns out to be irrecoverable, a remote wipe can be performed to erase any sensitive data from it.
Integrity
This component of data security involves ensuring the authenticity of data is maintained throughout its life cycle. Preserving data integrity means safeguarding data from unauthorized changes. Cybercriminals, in man-in-the-middle attacks, can modify data in transit, causing information to be altered, resulting in miscommunications between the sender and receiver, and leading to sensitive data losing its value. The following measures can be taken to maintain data integrity on mobile endpoints:
- Separate and containerize: Clearly define and separate the corporate workspace from the personal space through containerization to ensure there is no mixture of work and personal files. This allows the IT team to fully monitor the corporate workspace while ensuring privacy on the personal space.
- Encrypt with VPN and certificates: Configure a work VPN app on mobile endpoints and enable the use of strong encryption algorithms like FileVault encryption on Mac devices to ensure that data is protected at rest, in use, and in transit.
- Restrict automatic backup features: Disable apps from creating automated cloud backups, protecting the data from any threats it might face in third-party cloud storage.
- Verify endpoints: Allow only verified mobile devices to connect to the work network, protecting it from being accessed by unauthorized devices. It is possible to prevent rooted or jailbroken devices from connecting, and even ensure that the corporate Exchange account is accessed from only verified devices to further protect data.
Availability
Keeping data available means to keep it accessible to those who need it. Unintended system downtime is one factor that affects data availability and, in turn, the productivity of employees. Here are a few measures that can be taken to ensure data availability:
- Scheduled updates: Schedule app and system updates for non-work hours to ensure that devices are properly updated, but employee productivity is minimally impacted. Moreover, employees can be informed of when updates are scheduled so they can ensure they are connected to a stable connection with the required bandwidth.
- Group-based resource distribution: It may be something of an overwhelming task for IT admins to handle multiple resource requests from various teams at the same time. However, through MDM, distributing resources to endpoints is made easier by enabling distribution to directory groups instead of individual employees. Distributing requisite resources this way ensures each team has timely access to the files it needs, eliminating the possibility of shadow IT.
- Remote troubleshooting: Ensure availability is not interrupted by remotely troubleshooting employee devices, thus resolving any technical issues from the management console.
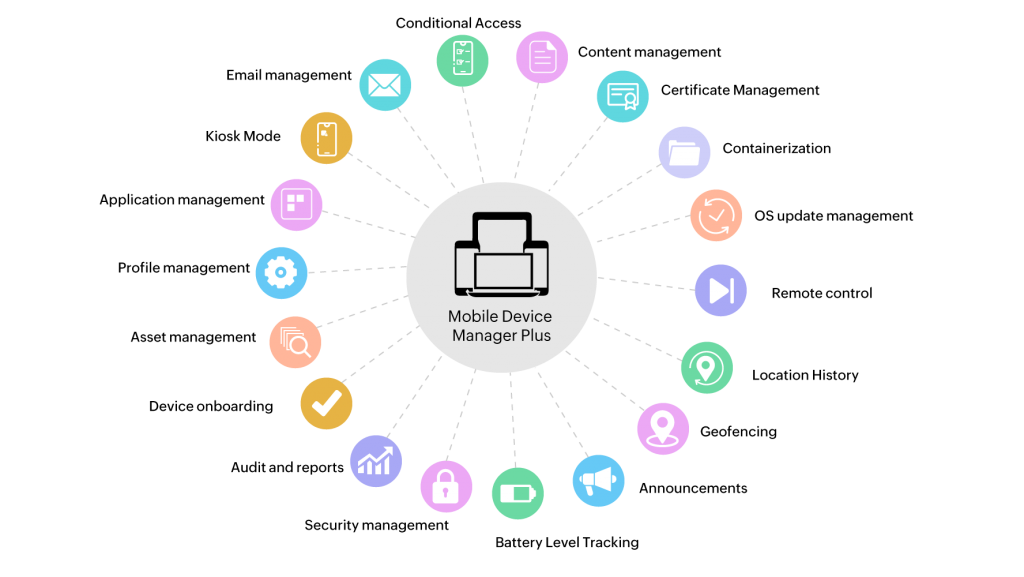
Mobile Device Manager Plus: The Comprehensive MDM Solution
ManageEngine’s Mobile Device Manager Plus, is a robust and powerful MDM solution that helps IT admins securely manage corporate and personally owned devices operating under the Apple, Android, Windows, and Chrome Operating System. In addition to enabling IT admins to ensure enterprise-grade security on mobile endpoints, Mobile Device Manager Plus makes every stage of a device’s life in the organization easier.



Leave a Comment